Network devices
Workstation - a computer intended for individual use that is faster and more capable than a personal computer and it is a standalone machine.
Function: It will perform a certain set of tasks like photo editing, video production or audio recording.
A network interface card (NIC) is a circuit board or card that is installed in a computer so that it can be connected to a network.
Function: A network interface card provides the computer with a dedicated, full-time connection to a network. Personal computers and workstations on a local area network (LAN) typically contain a network interface card specifically designed for the LAN transmission technology
Print
Feature
Function
Mail
Feature
Function
Web
Feature
Function
Proxy
Feature
Function
File
Feature
Function
Interconnection devices
Router
Purpose
Feature
Function
Switch
Purpose
Feature
Function
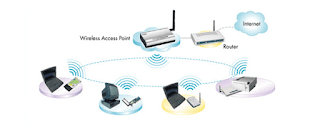
Wireless Access Point
Purpose
Feature
Function
References
Workstation
https://techterms.com/definition/workstation [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
Definition Workstation
https://searchmobilecomputing.techtarget.com/definition/workstation [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
Definition network interface card (NIC)
https://searchnetworking.techtarget.com/definition/network-interface-card [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
Bus network topology diagram
https://conceptdraw.com/a878c3/preview--Bus%20network%20topology%20diagram [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
3.6.4. Network Interface Cardhttps://informatics.buzdo.com/p480-network-card.htm [Accessed on 29th may 2018]
3.6.4. Network Interface Cardhttps://informatics.buzdo.com/p480-network-card.htm [Accessed on 29th may 2018]
TP-Link Archer C7 AC1750 Wireless Dual Band Gigabit Router (V2)
https://www.pcmag.com/review/352074/tp-link-archer-c7-ac1750-wireless-dual-band-gigabit-router [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
Network Switch Diagram Template
https://www.lucidchart.com/pages/examples/network-diagram/network-switch-diagram-template [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
Wireless Networking Simplified: The Terms You Should Know
https://www.makeuseof.com/tag/wireless-networking-simplified-the-terms-you-should-know/ [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
How to use Google Cloud Print to make printing from Android a dream
https://www.techrepublic.com/article/pro-tip-use-google-cloud-print-to-make-printing-from-android-a-dream/ [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
Email Administrator's Guide
http://death2spam.com/docs/admin/index.html [Accessed on 29th May 2018]
Web Diagram Examples - Include conceptual website, web site map, web architecture.
https://www.edrawsoft.com/Web-Diagram-Examples.php [Accessed on 29th May 2018]